The environmental problems our planet faces due to the combustion of fossil fuels is a growing concern. Fossil fuel technologies impact our environment through the generation of green house gases in the process. The depletion of fossil fuels, nonetheless, is a concern by itself. Technologies for clean energy generation using sustainable energy sources can address both these separate issues together, which if realized would be one of the greatest feets and problem science could solve.
Sunlight is the greatest and plentiful sustainable energy source. Harvesting sunlight for clean energy generation could indeed help to reduce CO2 emissions (which is one of the green house gases) and lessen society’s impact on the environment. Scientists have been working to develop energy harvesting technologies mimicking what plants do in their process called photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants produce energy from sunlight. Mimicking photosynthesis using man-made materials is called “artificial photosynthesis“.
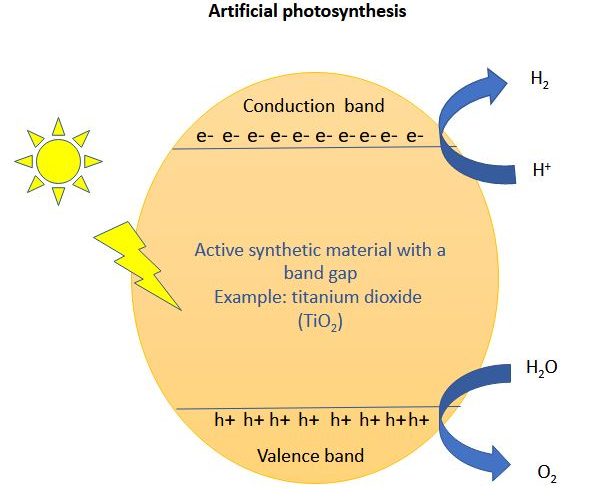
Among the various methods proposed to generate clean energy, photocatalytic water splitting is showing much promise. This method utilizes solar energy to split water (H2O) molecules and obtain dihydrogen (H2). The H2 can then be used as a carbon-free fuel or as raw material in the production of many important chemicals.
In the developing technologies, a man-made material is used to capture sunlight and the energy from that is used to split water into dihydrogen and oxygen. The technological bottleneck in such technologies is the limitations of the material to capture sunlight. The science behind capturing sunlight is based around a property called band gap of the materials. The extend of this band gap decides how much and what part of light in sunlight is captured/absorbed for the process. This is because sunlight has a wide range of energy components. For the naked eye, sunlight looks white light or colorless light. However, in energy terms it is composed of lights of different energy or wavelengths -vibgyor. Each colored light in vibgyor represents different energy range.
Currently, the limitation of solar light harvesting technologies is, the materials used can only use the ultraviolet energy range of sunlight (The ultraviolet light unfortunately constitutes only less than 5% of the sunlight). This is because we don’t have ideal materials with band gaps that could absorb the whole range of sunlight energy. Therefore, one important part of research is dedicated in band-gap tuning. Other strategy is to use organic dyes along with the band gap material that could absorb other range of sunlight and use that energy for the required internal complex chemical processes that facilitates photocatalysis.
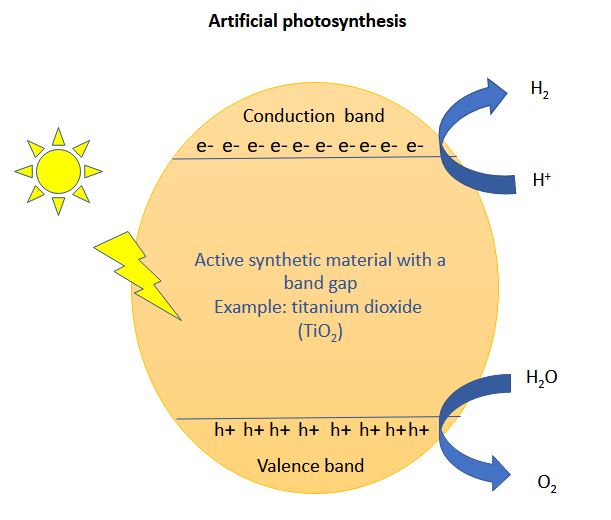
If you want to read more on current developments and technologies in photocatalytic splitting of water, click this link Integrating nanomaterial with light-absorbing molecule powers hydrogen production from water and sunlight.